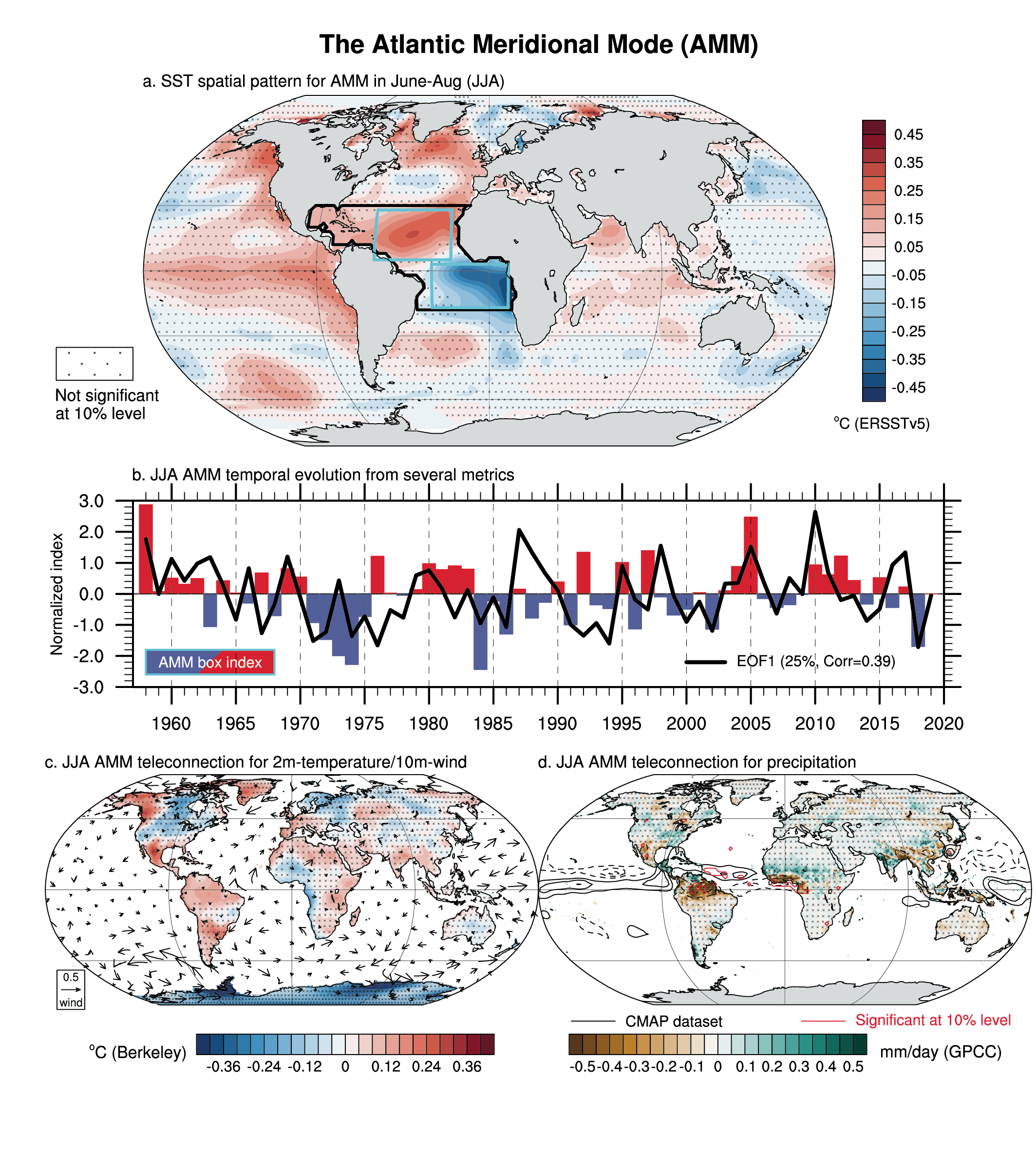
Annex IV Figure 7
Figure caption
Figure AIV.7 | The boreal summer Atlantic Meridional Mode (AMM) defined by June–July–August (JJA) standardized sea surface temperature (SST) difference between the north (5°N–30°N, 20°W–60°W) and south (5°N–20°S, 5°E–25°W) tropical Atlantic Ocean shown by the cyan boxes in (a) or estimated as the leading empirical orthogonal function (EOF) over the tropical Atlantic Ocean (the region denoted by the black box in a) for 1958–2019 using ERSSTv5. (a) SST anomalies regressed onto the AMM time series, which is shown in (b) as red and blue bars, while the black curve represents the leading principal component time series. Explained variance and correlation between indices are given in the legend in (b). (c) Same as (a) but for land surface air temperature (shading; based on Berkeley Earth) and 10 m level wind (arrows; m s–1 based on JRA-55 for 1958–2019) anomalies. (d) Same as (a) but for precipitation anomalies (shading based on GPCC for 1958–2016 and contours based on CMAP for 1979–2019 for every 0.2 mm day–1). On maps, no overlay indicates regions where the regressions are significant based on t-test accounting for false detection rates at 10% and crosses indicates no significance. Significance for CMAP precipitation is materialized by red contours in (d). All fields have been linearly detrended prior to computation.