Figure 3.1
Figure caption
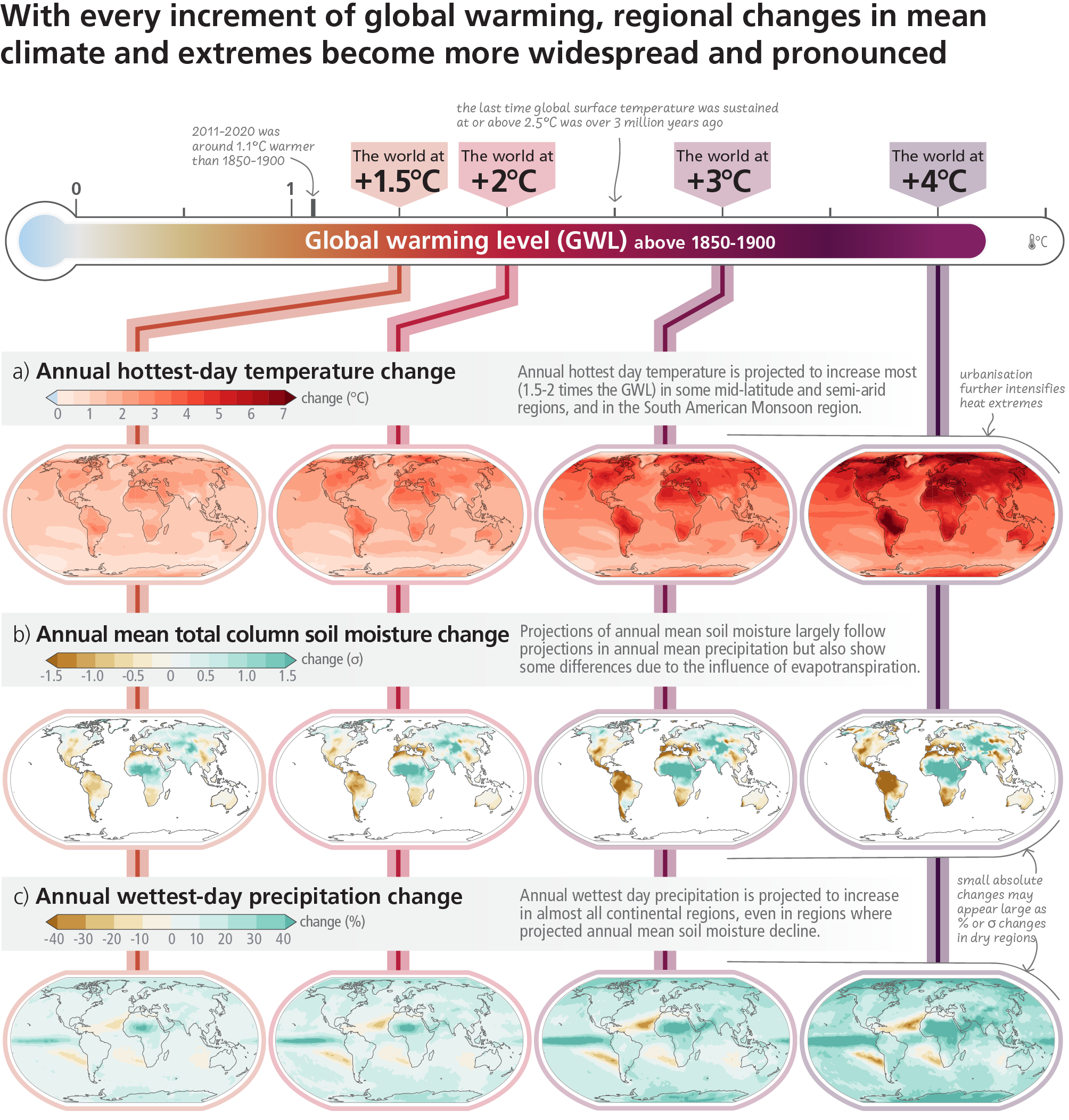
Figure 3.1: Projected changes of annual maximum daily temperature, annual mean total column soil moisture CMIPand annual maximum daily precipitation at global warming levels of 1.5°C, 2°C, 3°C, and 4°C relative to 1850–1900. Simulated (a) annual maximum temperature change (°C), (b) annual mean total column soil moisture (standard deviation), (c) annual maximum daily precipitation change (%). Changes correspond to CMIP6 multi-model median changes. In panels (b) and (c), large positive relative changes in dry regions may correspond to small absolute changes. In panel (b), the unit is the standard deviation of interannual variability in soil moisture during 1850–1900. Standard deviation is a widely used metric in characterising drought severity. A projected reduction in mean soil moisture by one standard deviation corresponds to soil moisture conditions typical of droughts that occurred about once every six years during 1850–1900. The WGI Interactive Atlas (https://interactive-atlas.ipcc.ch/) can be used to explore additional changes in the climate system across the range of global warming levels presented in this figure.{WGI Figure SPM.5, WGI Figure TS.5, WGI Figure 11.11, WGI Figure 11.16, WGI Figure 11.19} (CSB.2)