The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change brings together experts from all around the world.
Representatives of IPCC member governments meet one or more times a year in Plenary Sessions of the Panel. They elect a Bureau of scientists for the duration of an assessment cycle. Governments and Observer Organizations nominate, and Bureau members select experts to prepare IPCC reports. They are supported by the IPCC Secretariat and the Technical Support Units of the Working Groups and Task Force. Find out more about these roles below:
- Panel and Focal Points
- Observer Organizations
- IPCC Bureau
- Executive Committee
- IPCC Authors
- Expert Reviewers
- Secretariat
- Technical Support Units
Structure of the IPCC
The following graphic depicts the structure of the IPCC: 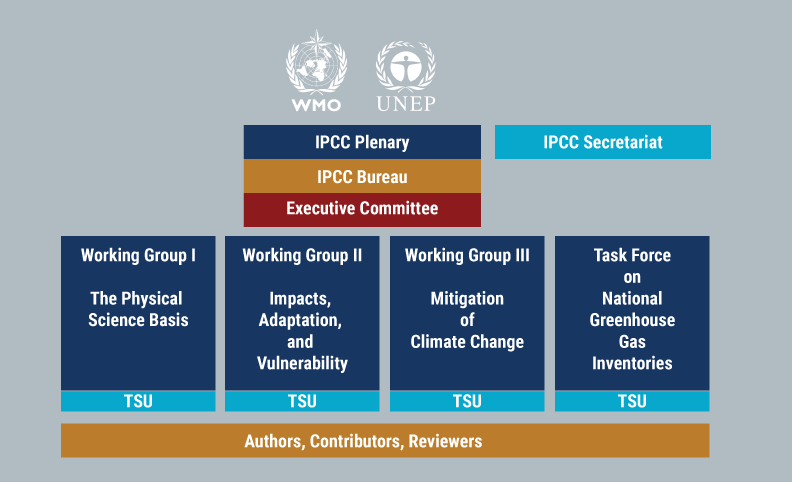
The Panel and the Plenary Sessions
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change is a panel of 195 member governments. Each IPCC member designates a National Focal Point. In cases where a country has not identified a Focal Point, all correspondence from the IPCC is directed to the Ministry of Foreign Affairs. Representatives of IPCC member governments meet in Plenary Sessions at least once a year. The Sessions are attended by hundreds of officials and experts from relevant ministries, agencies and research institutions from member countries and from Observer Organizations. The Panel works by consensus to decide on the organization’s budget and work programme; the scope and outline of its reports; issues related to principles and procedures of the IPCC; and the structure and mandate of IPCC Working Groups and Task Forces. The Panel also approves and adopts IPCC reports and elects the IPCC Chair, other members of the IPCC Bureau and the Task Force Bureau.
National Focal Points
IPCC National Focal Points prepare and update the list of national experts to help implement the IPCC work programme. The Focal Points also arrange for the provision of integrated government comments on the accuracy and completeness of the scientific and/or technical content and the overall scientific and/or technical balance of drafts of reports. They serve as the point of contact between the IPCC and its member governments. IPCC Focal Points are designated by an official letter from the Ministry of Foreign Affairs or the appropriate authority in the country. The list of IPCC National Focal Points is available here.
Observer Organizations
Any non-profit body or agency qualified in matters covered by the IPCC, whether national or international, governmental or intergovernmental, may be admitted as an IPCC Observer Organization. UN bodies and organizations are admitted as observers if they so request, and organizations with an existing observer status with the WMO or the UN may be considered as observers of the IPCC, subject to acceptance by the Panel. Representatives of observer organizations may attend sessions of the IPCC and the plenary sessions of the IPCC Working Groups. They are also invited to encourage experts to review draft IPCC reports. These experts participate in the review process in their own name and not on behalf of the Observer Organization.
The policy and process for admitting Observer Organizations is available here [ English | Arabic| Chinese | French | Russian | Spanish ].
The list of IPCC Observer Organizations is available here.
The IPCC Bureau
The Panel elects a Bureau to provide guidance to the Panel on the scientific and technical aspects of its work, advise on related management and strategic issues, and take decisions on specific issues within its mandate. The Bureau is made of the IPCC Chair, IPCC Vice-Chairs, the Co-Chairs and Vice-Chairs of the three Working Groups and the Co-Chairs of the Task Force on National Greenhouse Gas Inventories. It currently has 34 members. None of them is paid by the IPCC. Members of the Bureau are elected by the Panel for the duration of an assessment cycle and must reflect a balanced geographic representation, with due consideration for scientific and technical requirements. The Co-Chairs and Vice-Chairs of each Working Group form the Bureau of that Working Group. See the full list of the IPCC Bureau here
The Task Force Bureau (TFB)
The Task Force on National Greenhouse Gas Inventories (TFI) has its own Task Force Bureau (TFB) composed of 12 members and the two Co-Chairs of the TFI. The TFB oversees the National Greenhouse Gas Inventories Programme. The term of the TFB is normally the same as the term of the IPCC Bureau, and its members are elected at the same Session at which the IPCC Bureau is elected, unless decided otherwise by the Panel. Elections for the current IPCC Bureau and Task force Bureau were held during the 42nd Session of the IPCC in Dubrovnik, Croatia in October 2015. Results of the elections are available here.
The Executive Committee
The IPCC Chair, IPCC Vice-Chairs, and the Co-Chairs of the three Working Groups and the Task Force on National Greenhouse Gas Inventories form the Executive Committee (ExCom). The ExCom’s role is to strengthen and facilitate the timely and effective implementation of the IPCC work programme in accordance with the IPCC’s Principles and Procedures, the decisions of the Panel, and the advice of the Bureau. It includes as advisory members the head of the IPCC Secretariat and the heads of the Technical Support Units of the Working Groups and TFI. It meets regularly and its meetings are chaired by the IPCC Chair. The ExCom addresses issues related to IPCC products and its work programme that require prompt attention between Panel Sessions, and strengthens coordination between Working Groups and the Task Force on National Greenhouse Gas Inventories on activities related to the production of assessment reports and other relevant IPCC products. It also undertakes communication and outreach activities, and oversees the response to possible errors in completed assessments and other IPCC products based on the Error Protocol.
IPCC Authors and Review Editors
Hundreds of leading experts in the different areas covered by the IPCC reports volunteer their time and expertise as Coordinating Lead Authors (CLAs), Lead Authors (LAs) Contributing Authors (CAs) and Review Editors (REs) to prepare IPCC Reports. Authors are selected on the basis of their expertise following a call to governments, Observer Organizations and the IPCC Bureau for nominations and the submission of detailed CVs. After the nomination deadline, the Bureau of the relevant IPCC Working Group or Task Force selects the experts for these roles, taking into account the range of scientific, technical and socio-economic views and backgrounds, as well as geographical and gender balance. They also ensure that the teams include a mixture of experts with and without previous IPCC experience. This ensures that reports are not biased towards the perspective of any one region and that questions of importance to particular groups are not overlooked. Author teams may also involve experts from industry and from non-governmental organizations who can bring a valuable perspective to the assessment. Together, Coordinating Lead Authors and Lead Authors are responsible for the content of each chapter and draft specific sections based on their area of expertise. The Coordinating Lead Authors oversee the process and are responsible for the coordination of the chapters. There are usually two Coordinating Lead Authors per chapter, one from a developing and one from a developed country. The Lead Authors work in teams to produce the content of the chapter on the basis of the best scientific, technical and socio-economic information available. Coordinating Lead Authors and Lead Authors may enlist other experts as Contributing Authors to assist with their work. Hundreds of Contributing Authors provide specific knowledge or expertise in a given area in the form of text, graphs or data, and help ensure that the full range of views held in the scientific community is reflected in the report. Contributions may be solicited by Lead Authors but unsolicited contributions are also encouraged. In most cases, chapter teams are supported by Chapter Scientists, who provide technical and logistical support. For each IPCC report, authors produce two report drafts that undergo an external expert review. All the comments made during the review periods are collected and must be taken into account by the author teams when producing the subsequent draft. To support this process, each chapter team also has at least two Review Editors. They help identify expert reviewers, ensure that all substantive comments are afforded appropriate consideration, and advise Lead Authors on how to handle potential issues. These roles require considerable experience.
- IPCC Factsheet: How does the IPCC select its authors?
- Database of IPCC authors
Expert Reviewers
The IPCC is committed to preparing reports assessing the current state of knowledge of the science related to climate change that aim for the highest standards of scientific excellence, balance and clarity. To achieve this, each report undergoes two review periods: an Expert Review of the First Order Draft, and a Government and Expert Review of the Second Order Draft. This review process includes wide participation, with hundreds of reviewers commenting on the accuracy and completeness of the scientific assessment contained in the drafts. An Expert Reviewer may decide to comment on one section of the report, on a complete chapter or on the report as a whole. Beyond these official IPCC roles, thousands of scientists and experts worldwide contribute to IPCC assessments by adding to the body of scientific literature. Thousands of peer-reviewed articles in scientific journals and technical publications provide the essential foundation for IPCC assessments.
- IPCC Factsheet: What is an Expert Reviewer of IPCC?
The Secretariat
The Secretariat coordinates and assists the work of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. It organizes IPCC Plenary, Bureau and Executive Committee meetings and provides administrative support for these, including the preparation of documents and reports. It supports, as required, the Working Groups, the Task Force on National Greenhouse Gas Inventories, and any other task force, task group or committee established by the IPCC in the organization of their activities and meetings. The Secretariat also manages the IPCC Trust Fund and any other Funds agreed by the Panel, including budgeting, contributions to the IPCC Trust Fund, management of expenditure, auditing and reporting, consistent with WMO regulations and rules, and manages contractual and legal matters related to the IPCC. It manages the support for travel of delegates and experts eligible for support from the IPCC Trust Fund and assists with the necessary arrangements. Other tasks include:
- providing information management for the IPCC, including the archiving of IPCC reports and material used for their preparation, in accordance with the Principles and Procedures of the IPCC and in co-operation with the Technical Support Units;
- contributing to the implementation of the IPCC Protocol for addressing possible errors, the IPCC Communication Strategy and the Conflict of Interest Policy; in accordance with its responsibilities contained in these documents;
- providing the principal point of contact for members of the IPCC and Observer Organizations;
- promoting and maintaining cooperation, as principal IPCC contact point, with the UN system, in particular with UNFCCC; and liaising with the two parent organizations, WMO and UNEP;
- participating, through the Secretary of the IPCC, in the IPCC Executive Committee as an Advisory Member;
- undertaking any other tasks as required to support the IPCC in fulfilling its mandate as assigned by the Panel, the IPCC Bureau or the Executive Committee.
The Secretariat is located in Geneva, Switzerland, in the building of the World Meteorological Organization. Terms of Reference of the IPCC Secretariat and the Technical Support Units
Technical Support Units
Each Working Group and the Task Force on National Greenhouse Gas Inventories is supported by a Technical Support Unit (TSU). The TSUs provide scientific, technical and organizational support and support the Co-Chairs and Bureaux in the preparation and production of all relevant IPCC products. A TSU may also be formed to support the preparation of a Synthesis Report or any other Task Force constituted by the Panel. The IPCC TSUs also contribute to the implementation of the IPCC Protocol for addressing errors, the IPCC Communication Strategy and the Conflict of Interest Policy, in accordance with their responsibilities contained in these documents. They participate, through their TSU heads, in the IPCC Executive Committee as Advisory Members and undertake any other task as required by the Co-Chairs, or the IPCC Chair in the case of the Synthesis Report, to assist them in fulfilling their IPCC roles. The TSUs for the seventh assessment cycle are hosted by France (Working Group I); The Netherlands and Singapore (Working Group II), the United States of America and Malaysia (Working Group III) and Japan (Task Force on the National Greenhouse Gas Inventories). The Working Group I TSU has a satellite office in China, Working Group II in Singapore and Working Group III in Malaysia.